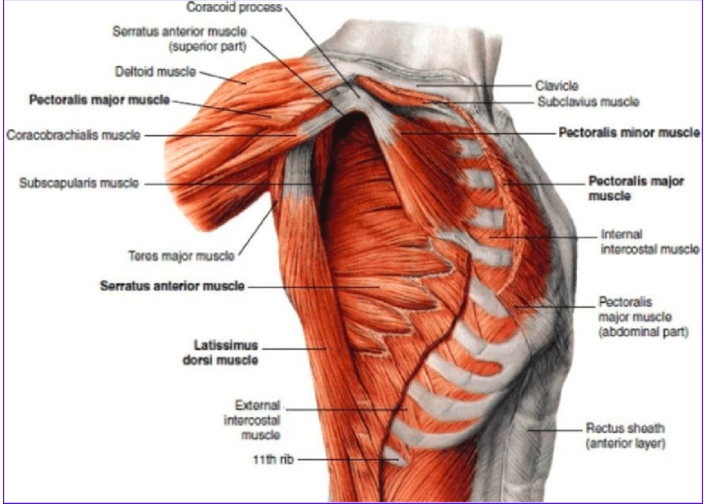
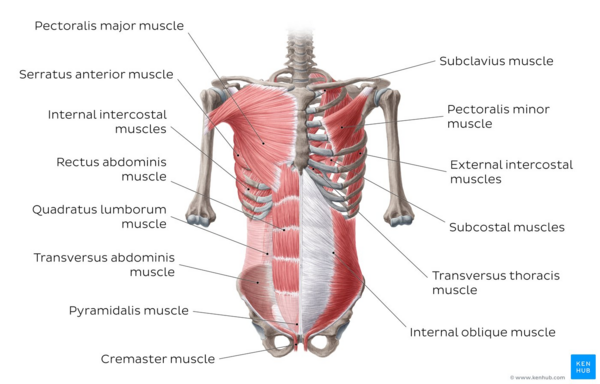
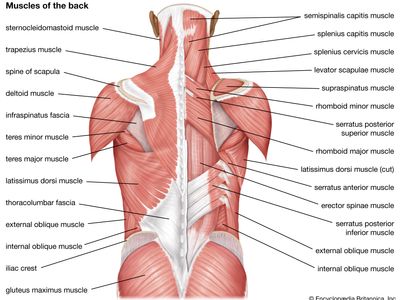
Muscles of the neck and shoulder may get strained due to prolonged stress in the area. You need to relax the area by slow movements and bring the muscle out of the overcontracted state.
Based on the location of the shoulder pain, the corresponding muscles, whether overstrained or overstretched, could be treated accordingly.