The movement that decreases the angle between joints.
Plantarflexion is generally considered to be the action that produces a simultaneous inferior displacement of the toes and superior displacement of the heel; dorsiflexion would be the opposite action.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/plantarflexion
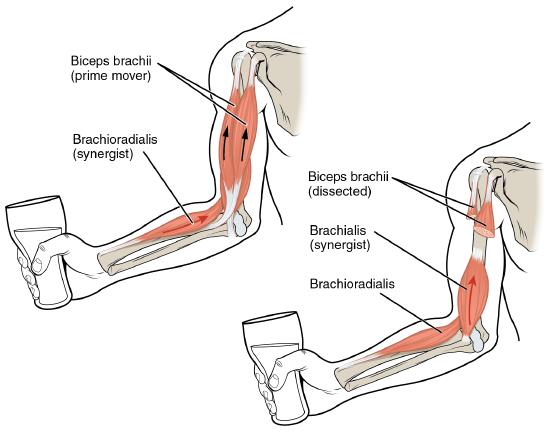
(also, prime mover) muscle whose contraction is responsible for producing a particular motion.Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover, or agonist/p>
(also, prime mover) muscle whose contraction is responsible for producing a particular motion.During forearm flexion (bending the elbow), such as lifting a cup, a muscle called the biceps brachii is actually the prime mover; however, because it can be assisted by the brachialis, the brachialis is called a synergist in this action.Also involved is the brachioradialis which assists the brachialis, and is also considered a synergist.
Synergist that assists an agonist by preventing or reducing movement at another joint, thereby stabilizing the origin of the agonist.
A synergist can also be a fixator that stabilizes the bone that is the attachment for the prime mover’s origin.
muscle that opposes the action of an agonist.A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb.
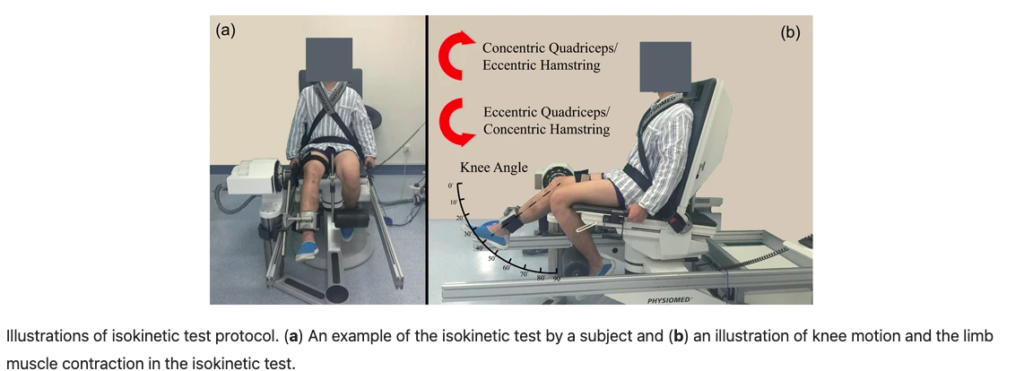
Isokinetic exercise involves maintaining a constant speed during muscle contraction, with the resistance provided by the machine adjusting to match the force exerted by the individual.
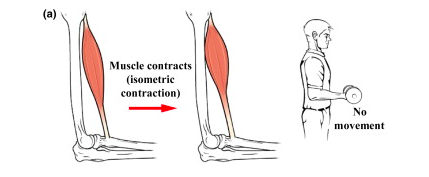
Types of muscle contraction. (a) Isometric contraction. Muscle produces the same amount of force as the external load (or opposing force); hence, no movement occurs.
Contractions can be described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains the same.
Images have been reproduced from OpenStax College, 2013. Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension. Connexions, 4 June 2013. http://cnx.org/content/m46470/1.3/.
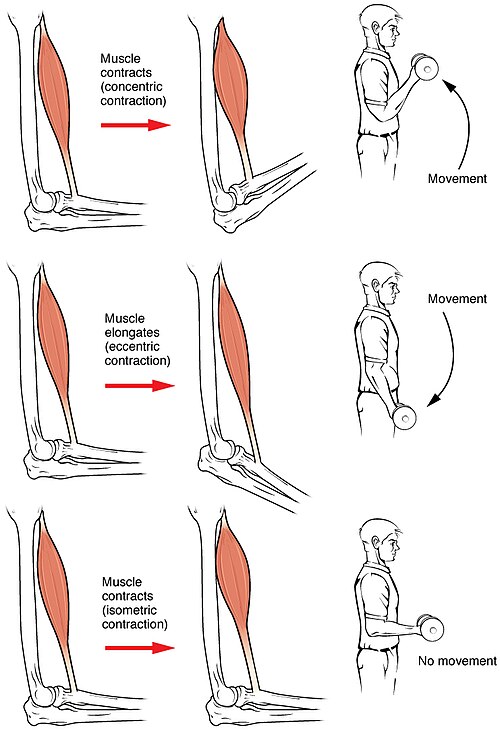
Isotonic contraction
In contrast, a muscle contraction is described as isotonic if muscle tension remains the same throughout the contraction. If the muscle length shortens, the contraction is concentric; if the muscle length lengthens, the contraction is eccentric.
In isotonic contraction, the tension in the muscle remains constant despite a change in muscle length.This occurs when a muscle’s force of contraction matches the total load on the muscle.
Concentric contraction
In concentric contraction, muscle tension is sufficient to overcome the load, and the muscle shortens as it contracts. This occurs when the force generated by the muscle exceeds the load opposing its contraction.
Eccentric contraction
In eccentric contraction, the tension generated while isometric is insufficient to overcome the external load on the muscle, and the muscle fibers lengthen as they contract. Rather than working to pull a joint in the direction of the muscle contraction, the muscle acts to decelerate the joint at the end of a movement or otherwise control the repositioning of a load.
Resistance Exercise (RE) is defined as a physical conditioning program that enhances fitness, health, and sports performance, using a variety of training modalities such as free weights, weight machines, medicine balls, elastic bands, and different movement velocities . The RE interventions including weighted lunges, hip abduction/adduction, knee extension/flexion, plantar-/dorsi-flexion, back extension, reverse chest fly, and abdominal exercises or a smaller number of compound movements of squats and deadlifts, target the major muscle groups attached to the hip and spine.
The Type of Resistance Exercise Training Program.
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Isometric RE | A static contraction of muscle against external resistance without change in its length or joint motion | Yoga poses such as Plank or the Warrior variations, side bridge, hundred breaths exercise, pushing against a fence |
| Isotonic RE | A dynamic exercise against resistance as a muscle lengthens or shortens through the available range of motion | |
| - Concentric contraction: an active muscle undergoes shortening while overcoming external resistance | Contraction of biceps curl with fixed weight | |
| - Eccentric contraction: an active muscle undergoes lengthening while being overcome by an external resistance | Extension of quadriceps during knee bend | |
| Isokinetic RE | An active exercise in which a muscle or group of muscles contracts against a controlled accommodating resistance that is moving at a constant angular velocity | Fitness machines (e.g., stationary bike, bench press machine, bent-over row), dynamometer |
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating calcium and phosphorus levels in the body, as well as bone health. It’s naturally produced in the kidneys and is also available as a synthetic medication to treat various conditions like hypocalcemia, osteoporosis, and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
-
Calcium Homeostasis:Calcitriol plays a major role in regulating calcium levels in the body by influencing calcium absorption in the gut, calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, and calcium mobilization from bone.
The amount of phosphate in your blood is also linked to your levels of:
- Calcium. When blood calcium levels increase, phosphate levels decrease. And when calcium levels decrease, phosphate levels increase.
- Vitamin D. It helps your body use phosphate.
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH). This hormone is made by parathyroid glands in your neck. It helps balance phosphate and calcium levels in your blood.
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found in all tissues in the human body but is mostly concentrated in the bones, kidneys, liver, intestines, and placenta. It exists in different forms, depending on where it originates.
Its major function is to protect your intestinal tract against bacteria, aid in digestion, break down fats and some B vitamins, and promote bone formation.
High levels of ALP in the blood may indicate bone, liver, or bile duct disease.
When the liver is not functioning properly, ALP is released into the bloodstream. Additionally, any condition that affects bone growth or causes the increased activity of bone cells can increase ALP levels in the blood.
Vitamin D deficiency is usually accompanied by elevated levels of total alkaline phosphatase in the blood. However, it is not the best indicator of vitamin D deficiency.
1α-hydroxylase
1α-hydroxylase is a vital enzyme that converts vitamin D (specifically, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3) into its active form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol). This process is crucial for calcium homeostasis and other essential functions. The enzyme is primarily found in the kidneys but also expressed in various other tissues.
-
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH):PTH is a key regulator of 1α-hydroxylase, stimulating its activity when calcium levels are low.
Calcitonin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood by decreasing them. It works by opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone, which increases blood calcium levels.
Most humans depend on sun exposure to satisfy their requirements for vitamin D. Solar ultraviolet B photons are absorbed by 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin, leading to its transformation to previtamin D3, which is rapidly converted to vitamin D3. Season, latitude, time of day, skin pigmentation, aging, sunscreen use, and glass all influence the cutaneous production of vitamin D3. Once formed, vitamin D3 is metabolized in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and then in the kidney to its biologically active form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Also known as Calcitriol.