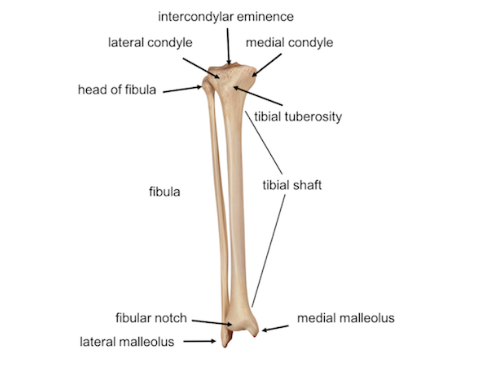
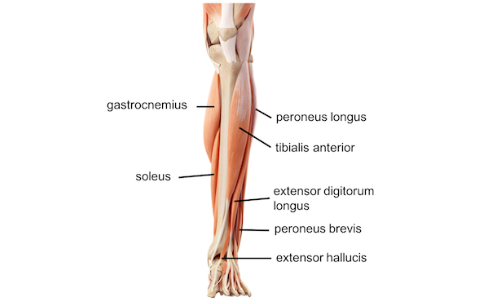
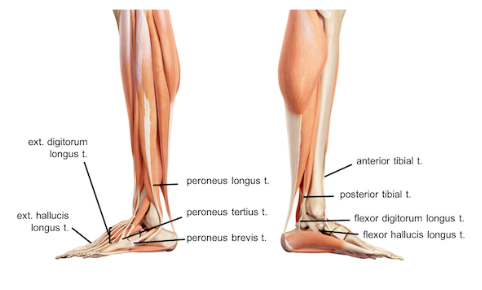
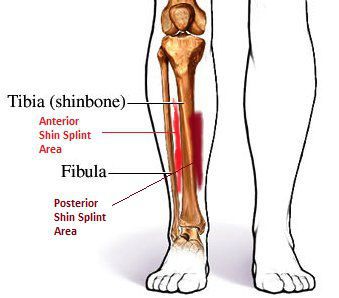
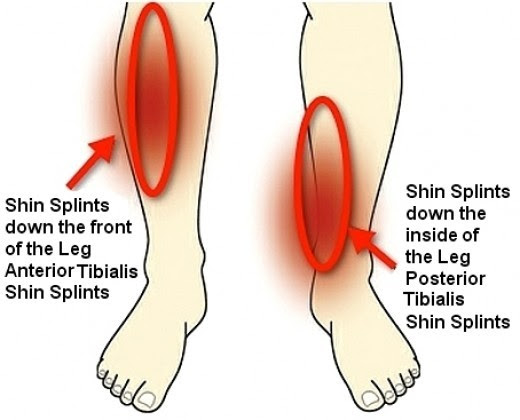
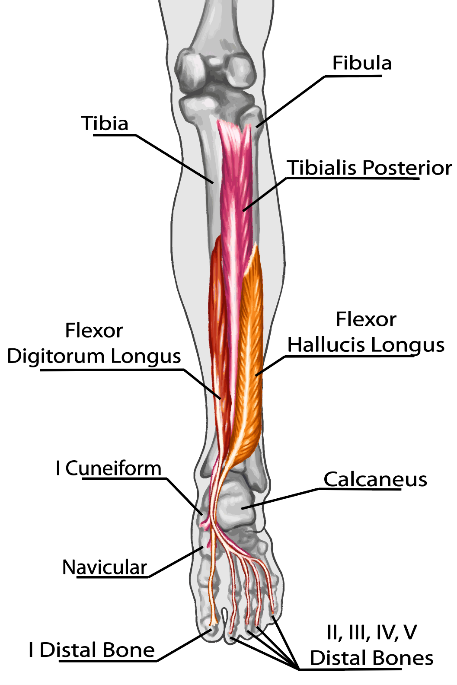
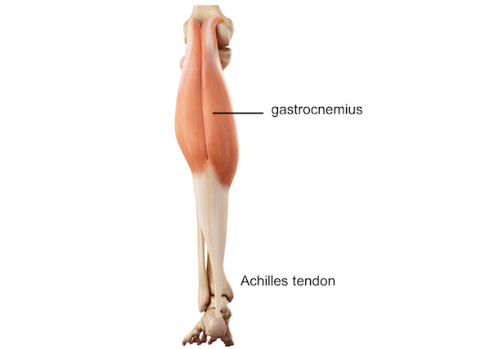
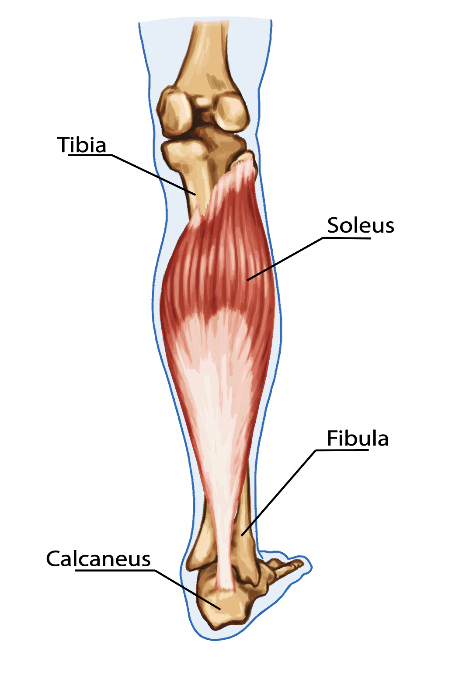
Shin splints is a type of shin pain, usually caused by a new regimen/exercise. Shin splints refer to pain and tenderness along or just behind the large bone in the lower leg (the tibia).
Symptoms
-
Pain felt on the front and outside of the shin. It’s first felt when the heel touches the ground during running. In time, pain becomes constant and the shin is painful to the touch.
Causes
Shin splints happen when you’ve put too much stress on your leg.
You’re more likely to get shin splints if:
- you have started exercising after not being active for some time
- you run or jump on hard surfaces
- you do not have a good running technique
- Repetitive hard exercise, sports, or activity can lead to inflammation of the muscles, tendons, and thin layer of tissue covering the shin bones, causing pain.